初始化一个配置信息,postProcessBeforeInitialization和afterPropertiesSet用哪个
前言
今天偶然看到一个文章 一次由于八股文引起的内存泄漏,看到文章里面的改法是换接口,从BeanPostProcessor换成InitializingBean,以前背八股时候还真没注意这两者区别,只是感觉很奇怪,都是初始化过程中能用的回调函数,为什么要写两个接口呢?文章里面也没谈论这两个区别,本文就看一下他们区别是什么。
(我猜背八股的人有很多都没仔细了解过他们区别,只是知道有这么一堆函数)
如果要实现bean初始化时候,加载一个东西,用哪个接口?
按照以前的八股背法,反正这两个都是bean实例化之后调用的函数,放哪个不都一样么?
bean的生命周期是:beforeInstantiation,实例化,afterInstantiation,属性赋值,beforeInitialization,afterPropertisSet,初始化(init-method),afterInitialization。
但是八股没背的是 beforeInitialization 是针对每个bean都会调用的,afterPropertisSet只针对当前bean调用一次。
实验
一个很简单的类,两个接口都实现,看里面打印了多少次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor , InitializingBean {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor");
return bean;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
|
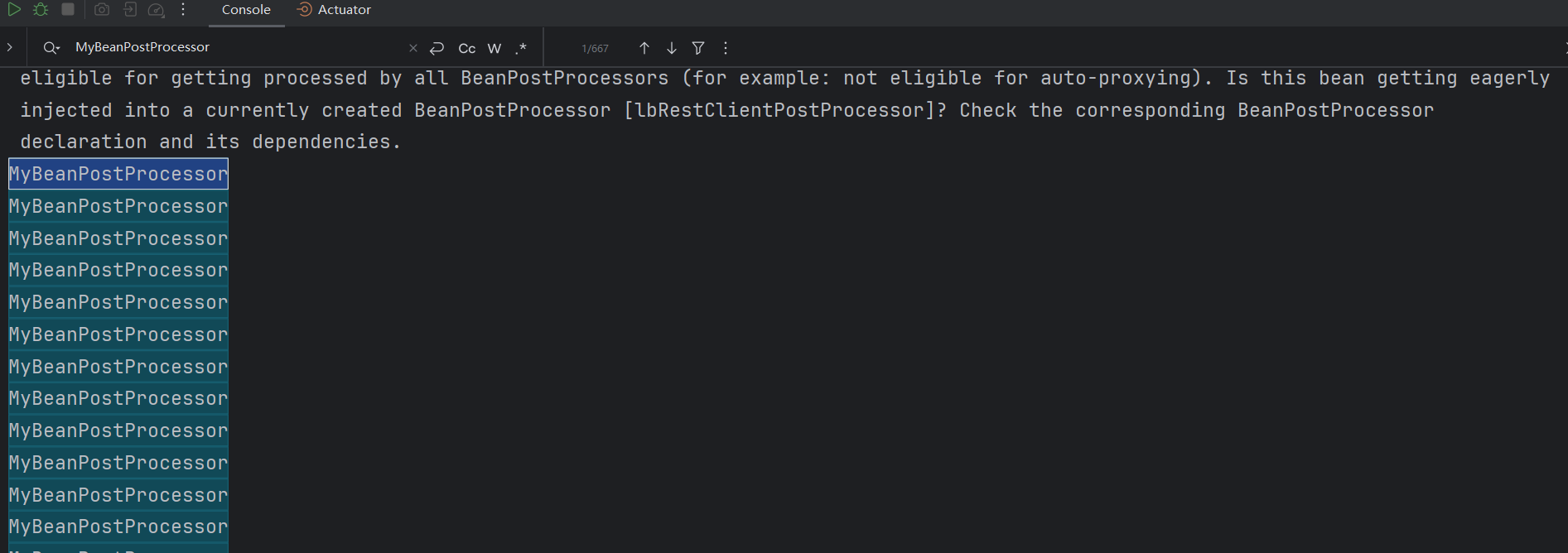
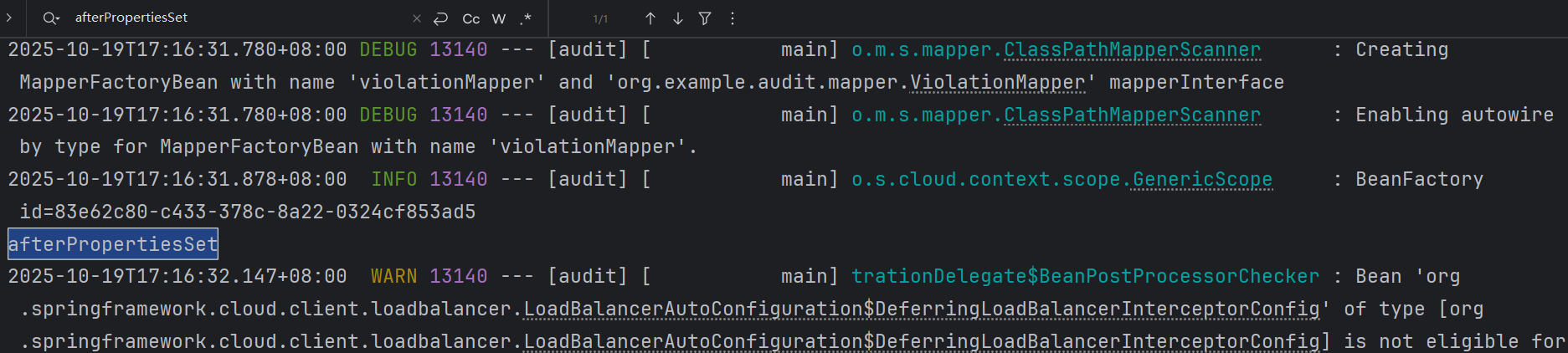
可以看到 afterPropertiesSet 只打印了一次,postProcessBeforeInitialization 打印了六百多次,应该是每个bean都调用了一遍。
下面看下spring源码,看看他是怎么调用的。
源码
完整的bean的创建流程之前写过,可以翻翻我之前的文章。 了解spring的bean创建过程
断点直接打到postProcessBeforeInitialization,print的地方,看堆栈是这个函数:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition)
doCreateBean会调用initializeBean,就在populateBean之后
1
2
3
4
5
|
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
|
也就是每个bean都会执行initializeBean,applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization就是调用回调函数的地方
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
|
进入applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization,可以看到代码里面getBeanPostProcessors拿了一个list
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
|
getBeanPostProcessors会直接返回成员变量beanPostProcessors,下面是beanPostProcessors的内容
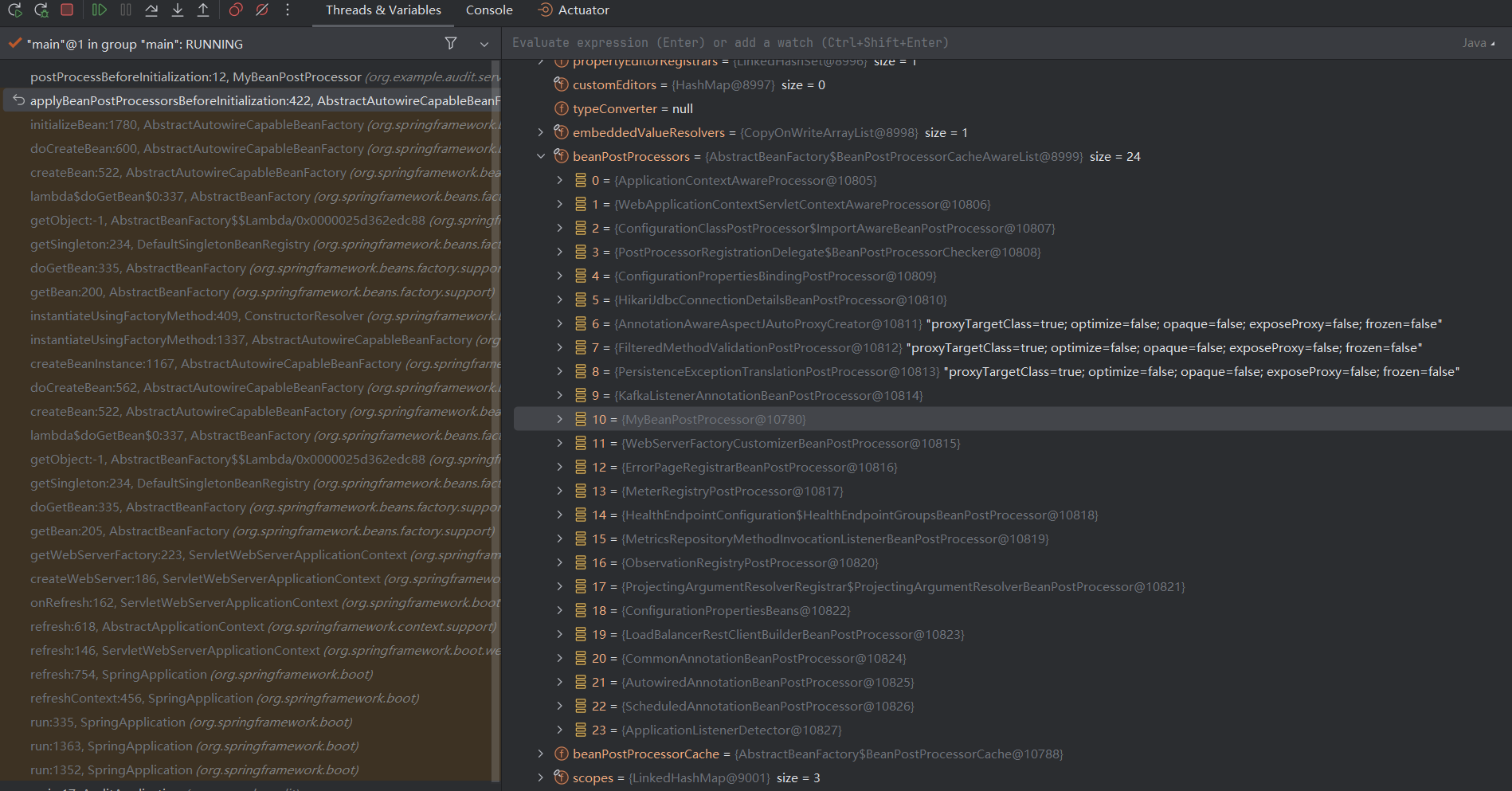
到这基本可以确定是每个bean都会执行一遍这个。
下面看一下 afterPropertiesSet 在哪调用的。
其实就在上面代码的下一行,invokeInitMethods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String[] initMethodNames = mbd.getInitMethodNames();
if (initMethodNames != null) {
for (String initMethodName : initMethodNames) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd, initMethodName);
}
}
}
}
}
|
现在就看出来了,调用的是当前bean的afterPropertiesSet。
结语
早期直接背了,没有深刻理解,这都是隐患,之后要还回来。赶紧看看项目代码里面有没有用错的地方。


